Plug in, Power up and Drive
EV Managed Charging Pilot Program
Electric vehicles adoption in Clark County is on the rise with more than 10,000 EV’s registered across our county as of March 2024, an increase of nearly 3,000 EV’s since March 2023. The early acceptance of electric, and plug-in-hybrid vehicles in the Pacific Northwest, combined with our low carbon electricity, makes us a sweet spot for electric-powered vehicles. Additionally, our low utility rates make electric vehicles cheap to operate and mild temperatures make it easier on your pocket book and batteries.
Consumers find several advantages to electric vehicle ownership. EV’s release no tailpipe emissions, reduce smoggy conditions on our roads and are noise free. Sales and models available have grown steadily over the past years. These days just about every auto manufacturer from Chevrolet to Mercedes is producing one or more models. They run the gamut from the thrifty Nissan Leaf to luxury Tesla models.
Calculate potential savings using our online calculator.
The CO2 emission rate is much lower for Electric Vehicles. See the table below for a comparison:
| Annual Emissions Per Electric Vehicle | |
|---|---|
| EV powered by Clark Public Utilities electricity | 1,260 pounds of emissions |
| Gasoline powered vehicle | 11,435 pounds of emissions |
Charger Information
Clark Public Utilities understands the importance of publicly available charging infrastructure and is proud to offer ChargePoint Level II chargers at both our Downtown Electric Center and Operations facility, with Level III (DC Fast Charging) at the downtown offices.
EV drivers buzzing around town have more charging options than just our utility locations. Locally you will find familiar places like U-Haul, Fred Meyer, Chuck’s Produce, Walgreens, Kohl’s and car dealerships outfitted with charging stations. A comprehensive list of chargers can be found using a variety of different websites and applications; Plug Share is a good website to start your search, as is EV Hype.
When planning long distance drives, map out your route so you don’t exceed your EV’s range between charges. Traveling up the I-5 corridor, you’ll find plenty of charging stations. To help plan a long trip or to find stations, visit the US Department of Energy Alternative Fuels Data Center.
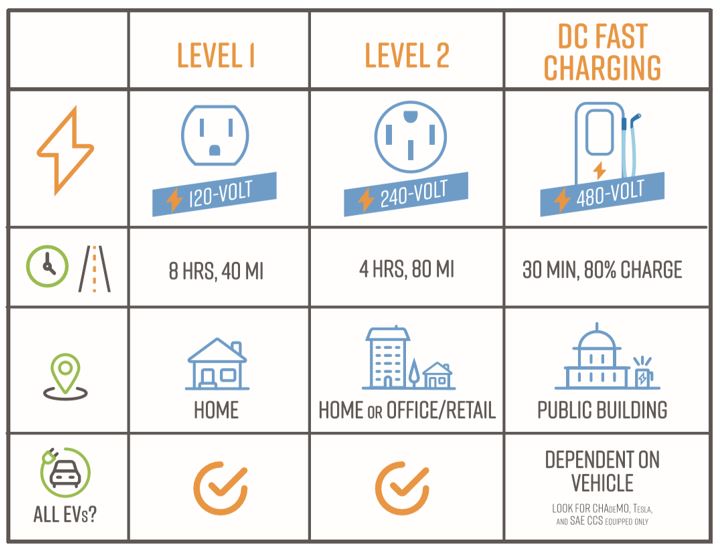
We know different charging levels can be confusing at times so we’ve created the below informational graphic to help customers better understand the three levels of EV charging.
Because the utility must plan for increased electric usage into the future it’s a good idea to alert us before installing a charger in your home. And you may learn your recent purchase qualifies for a Clark Public Utilities rebate!
If you’re interested in learning more about the benefits of electric vehicles, the following websites are a good place to start:
Electric Vehicle Incentives
To learn more about our EV incentive programs, check out our residential and commercial EV programs webpages.
EV Grant Opportunity Program (EV-GO)
- Clark Public Utilities will be offering grant funding to support the build out of publicly accessible EV charging infrastructure in Clark County.
- Available to Clark County municipalities, local government agencies located in Clark County, and Clark County non-profits.
- Grant can cover up to 50% of the project costs, including EV charging equipment, construction costs, and electric service upgrades.
- Funding is limited; contact Matt Babbitts at [email protected] (360)992-3365 with questions or to learn more details of the program
Transportation Electrification Plan
On March 2nd, 2021 the Clark Public Utilities Board of Commissioners adopted the first iteration of the utility’s Transportation Electrification Plan. An updated version of the Transportation Electrification Plan was developed in late 2023. The TE Plan identifies our utility’s objectives and strategies related to the adoption of EV’s in Clark County and EV related customer facing incentive programs.